New Study Finds That 15% of Americans Don’t Believe Climate Change is Real
|
Listen to this story:
|
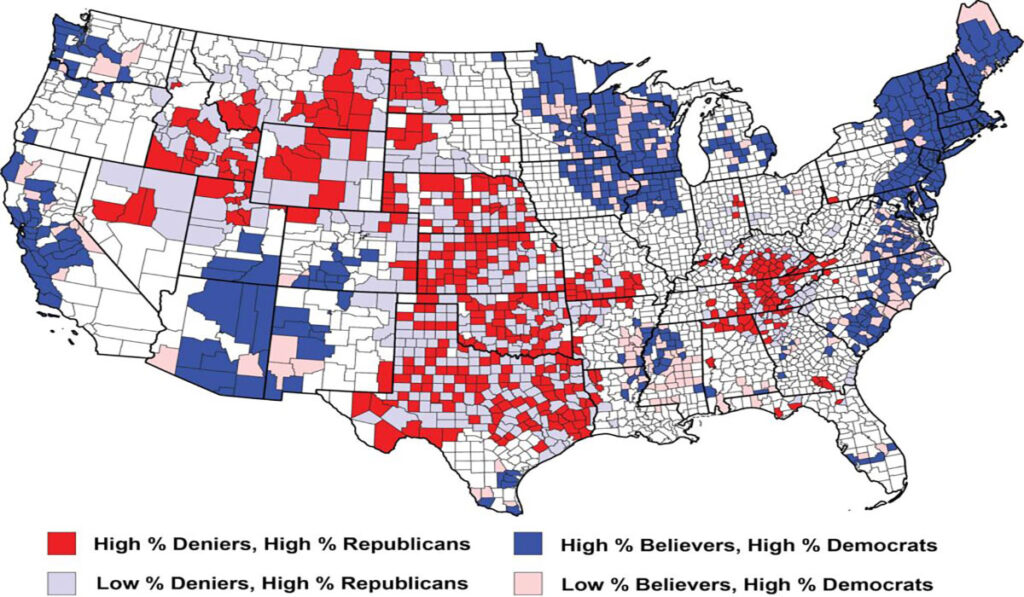
- Denialism is concentrated in the central US and South, with strong links to political affiliation, education level, and rural vs. urban residency.
- Platforms like Twitter, fueled by figures like Trump and conservative media, play a key role in spreading denialism.
- Addressing misinformation through education, policy, and social media platform accountability is crucial to combat denialism and build resilience to climate impacts.
Climate change denialism varies geographically within the U.S., with political ideology, economic dependency on fossil fuels, and mistrust in science being key contributing factors. Social media platforms serve as significant channels for influencers to disseminate misinformation. The study utilized Twitter data from 2017 to 2019 to estimate the prevalence of climate change denialism at state and county levels, identify typical profiles of deniers, understand the spread of denialism via social media, and examine the exploitation of events to foster climate change denial attitudes.
The research analyzed 7.4 million geocoded tweets from 1.3 million users, classifying them into categories of belief or denial regarding climate change. By employing a deep learning text recognition model, the study profiled climate change deniers and mapped influential networks on Twitter, offering insights into the dynamics of climate change discourse on the platform.
The study found that climate change denial is most prevalent in the central U.S. and the South, with significant variances within states. Political affiliation emerged as the strongest predictor of climate change denialism, followed by factors like education level and COVID-19 vaccination rates. The analysis also highlighted how social media networks, spearheaded by figures such as Donald Trump and supported by conservative media, play a critical role in disseminating climate change denialism.
The use of Twitter data to analyze public opinion on climate change reveals significant clusters of denialism, particularly in Republican and rural counties. The correlation between denialism and skepticism towards science indicates a broader challenge in addressing science-based public policies. The study underscores the need for targeted educational campaigns and policy interventions to counter misinformation and enhance community resilience against the impacts of climate change.
While the use of AI provides a novel tool for analyzing vast amounts of social media data, the study acknowledges limitations, including potential biases inherent in AI technologies and the challenges of accurately classifying ambiguous or sarcastic content. The ethical implications of using AI for research, especially in sensitive areas like climate change, are also discussed.
Related Article: Climate Change Trade-Offs: What Does it Take to Keep Our World Insurable? – Study by Allianz
This comprehensive study illuminates the complex social anatomy of climate change denialism in the U.S., emphasizing the role of social media in spreading misinformation. It calls for concerted efforts by policymakers, educators, and social media platforms to address the spread of climate change misinformation and foster a more informed public discourse.
In a related article by Aliya Uteuova, the importance of addressing climate change denialism is further underscored, with insights from climatologist Michael Mann, who emphasizes the need for scientists to counter misinformation actively. The role of social media platforms in monitoring and mitigating the spread of misinformation is highlighted as crucial in combating the misinformation that fuels climate change denialism.
This report sheds light on the significant challenge of climate change denialism in the U.S., offering critical insights into its social dynamics and the influential role of social media in shaping public opinion on this pressing global issue.
Read Full Report










